NIAC stands for NASA Innovative Advance Concepts, a program that rewards proposals it deems to be transformative for both robotic and human space exploration. Each of this year’s 12 winners receives $100,000 for Phase 1 development. For those that make it past the first year round of judging NASA provides an additional $500,000 over the next two years.
Two NIAC winners of note are concepts right out of the pages of science fiction novels. They are:
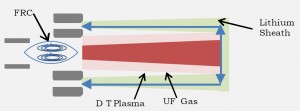
PuFF – a pulsed fission-fusion propulsion system. This is a technology that dates back to the birth of the hydrogen bomb which used a fission trigger to ignite fusion setting off the massive explosive. But Rob Adams of NASA Marshall Space Flight Center, would use fission to heat a fusion plasma. The combined energy from the two forces would pass through a magnetic field that would form a nozzle and generate thrust. The propulsion technology has promise for use in long-duration space exploration and is one of a number of nuclear-powered proposals that NASA is fielding.
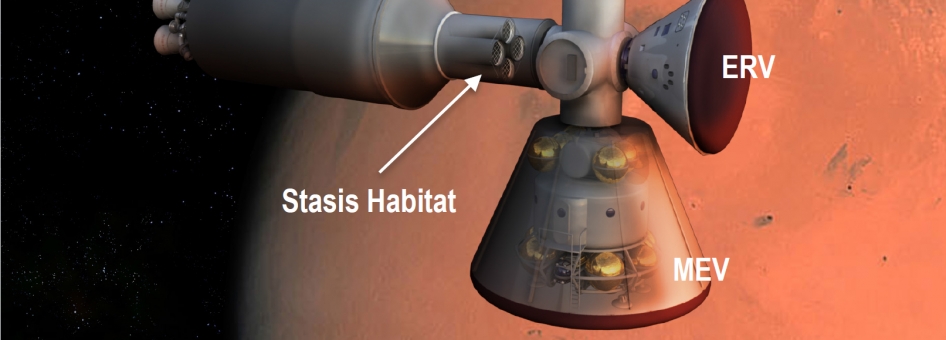
Stasis Habitat – Long duration human flight into Deep Space comes with lots of challenges. In many science fiction novels and movies crew complements are minimized by putting several members into suspended animation in which they are in a deep sleep with reduced metabolic rates. John Bradford of SpaceWorks Enterprises, Inc., is leading a project to design a torpor-inducing Mars transfer habitat, a pressurized module that would be attached to the living crew quarters in a Mars-bound space mission. For a human mission to Mars and beyond it would mean much of the crew would be placed into torpor, a deep sleep state and would only be awakened upon reaching the destination. This means crew space requirement volumes could be reduced by a factor of 10 in long missions. It means a smaller payload to orbit requirement from the gravity well of Earth. The new stasis habitat would be very small, pressurized and docked around a central node connecting the awake crew quarters and descent modules.
Other 2013 NIAC award winners include:
- Two-Dimensional Planetary Surface Landers;
- A Dual-mode propulsion system for CubeSat exploration of the Solar System;
- A design for a permanent habitat to be located at the L2 Earth-Moon Lagrange point;
- A new methodology for unlimited long endurance flights at high altitude;
- A new technology designed to map the interior structures of comets and other Deep Space objects;
- 3D printing technology to create in situ manufacturing using local organic and inorganic resources;
- Plasmonic force propulsion systems for use with small spacecraft;
- Robotic landers and rovers capable of changing form and function based on local requirements and circumstances;
- A high-atmosphere carrier balloon housing a 10-meter (33 foot) reflector telescope and capable of remote sensing and telecommunications;
- An electro-optical imaging sensor to replace bulky optical telescopes.