March 6, 2016 – The two biggest facilitators of Internet connectivity here in the second decade of the 21st century are smartphones and Wi-Fi networks. Slipping the tether of ethernet cables as the means of connectivity has led to an enormous expansion in Internet access. But conventional Wi-Fi requires an investment in combo routers and modems and contracts with Internet service providers.
Named by Massachusetts Institute of Technology as one of the breakthrough technologies of 2016, a new form of Wi-Fi will be unveiled in the next couple of weeks at NSDI ’16, in Santa Clara, California. This annual three-day symposium, representing the Advanced Computing Systems Association, will be the setting where Passive Wi-Fi will be demonstrated to the research and industry leaders in the fields of computing and Internet connectivity.
Passive Wi-Fi is the invention of a team of University of Washington researchers. In a paper to be presented at NSDI, the team will not only speak about but demonstrate the technology. The researchers set out to prove that Wi-Fi transmissions could be achieved using very little energy.
Those of you who use Bluetooth will ask how is it different?
Bluetooth is a low-energy technology for enabling inter device wireless communication. Passive Wi-Fi works similarly but at speeds 11 times faster than Bluetooth while using only one thousandth the power.
And compared to normal Wi-Fi, like the technology I have here in my home, we are talking one-ten-thousandth the power.
How does Passive Wi-Fi work?
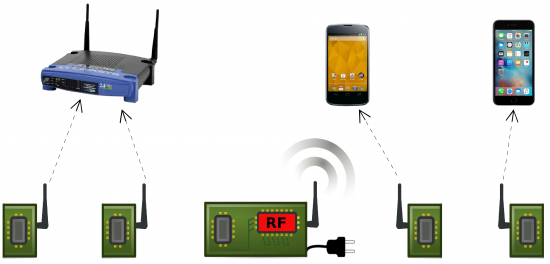
In traditional Wi-Fi every device has both digital and analog radio frequency technology on board. But Passive Wi-Fi only requires its communication Wi-Fi devices to have digital on board. The Wi-Fi power intensive function only exists with one plugged-in device. It continually broadcasts the Wi-Fi signal. The Passive Wi-Fi devices (see image below) use reflections of the signal and converts these to packets which are transmitted to any Wi-Fi receiving device such as a smartphone. Any Wi-Fi enabled device as far away as 30 meters (100 feet) can communicate with others. The signal can even travel through walls. The Passive Wi-Fi sensors can harvest energy from other radio frequency signals such as those produced by radio broadcasts and television.
So what kind of devices can use Passive Wi-Fi?
You name it: routers, smartphones, tablets, smart thermostats and more.
States Vamsi Talla, one of the inventors, “all the networking, heavy-lifting and power-consuming pieces are done by the one plugged-in device….the passive devices are only reflecting to generate the Wi-Fi packets, which is a really energy-efficient way to communicate.” This low energy way to communicate changes the Wi-Fi playing field opening up enormous possibilities for the Internet of Things (IoT). For smart homes it means only micro-watts of energy will be needed to control all the smart devices within them.
The inventors have launched a company called Jeeva Wireless to commercialize their communication breakthrough.